Face Inset
The Face Inset effect allows you to map a feature of your face (e.g. eyes) to other areas of your face. This allows you to, for example, replace your eyes with mouths or map an eye to the center of your forehead.
Create the Face Inset
To create a Face Inset object, first click the "+" button in the Objects panel. Then, select Face Effects -> Face Inset.
Adjust the Face Inset
The Face Inset object is a 2D object. Adding a new Face Inset automatically opens the 2D Scene View in the Scene Panel to visually edit the Face Inset.
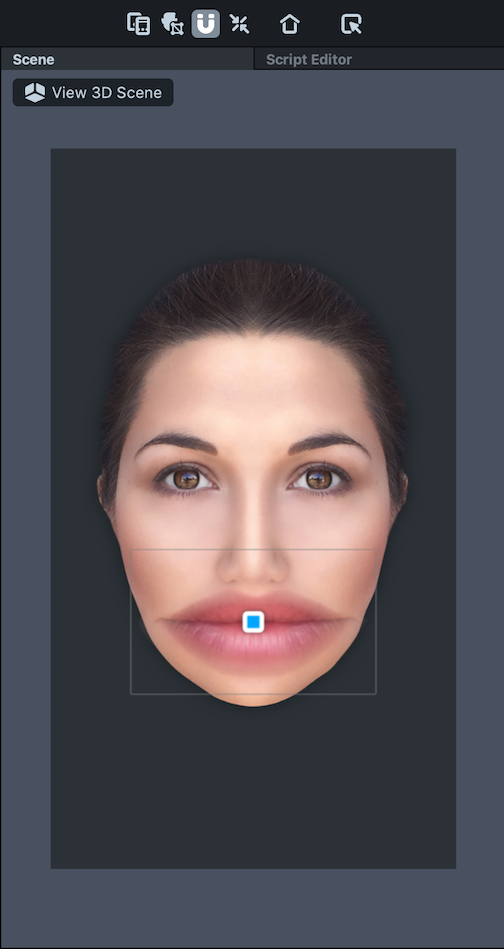
Once added, you should see a new Face Inset object in your Objects panel. It is a child of the Face Inset Binding object which binds the inset to your face. With the Face Inset object selected, move and scale the added face inset in the Scene panel to wherever you want on the face.
Drag the corner of the face inset to rotate.
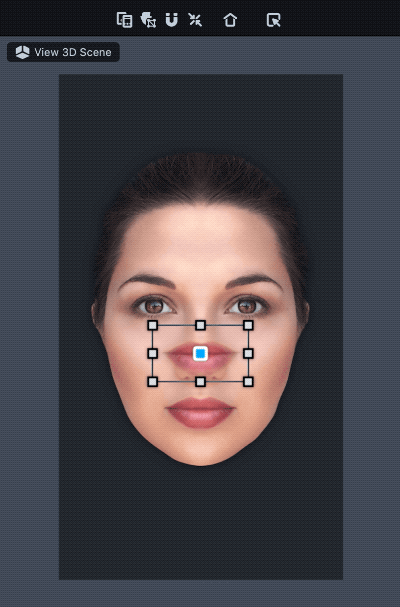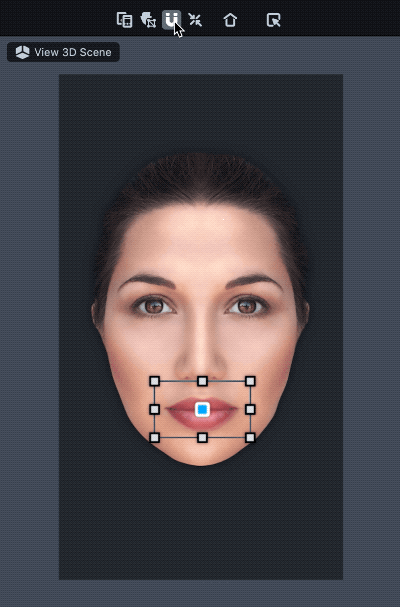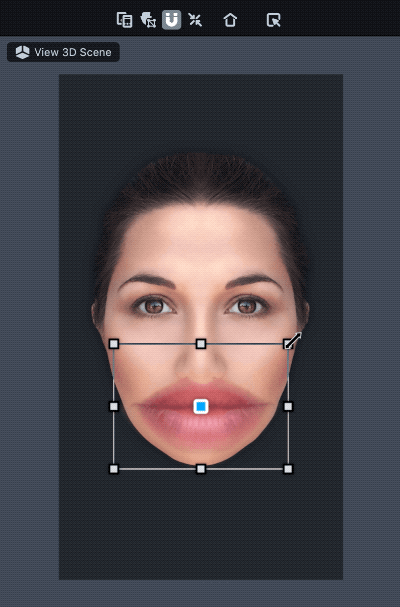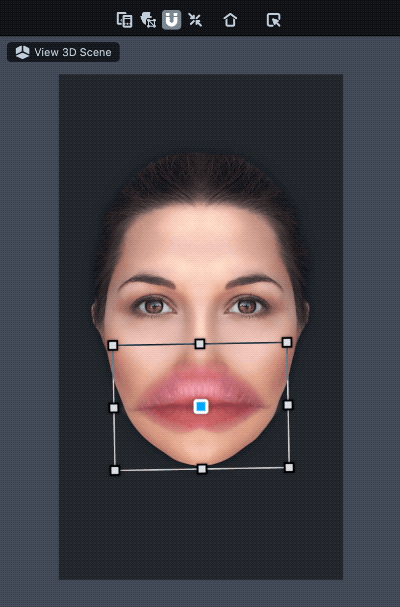
Face Inset Settings
With the Face Inset object selected, you'll see the following settings used to configure the object in the Inspector panel:
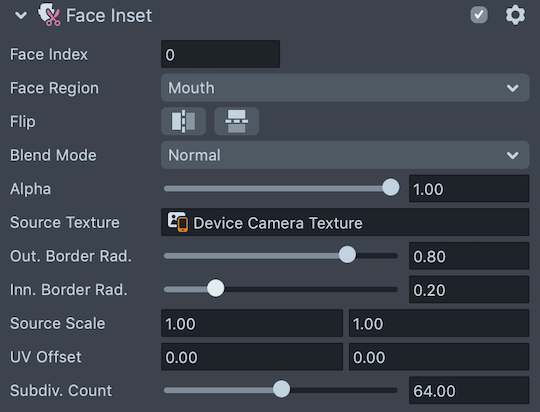
- Face Index - Which face the object will apply to. The first face in the scene is 0; the second face in the scene is 1
- Face Region - The region of the face you'd like to copy. Available options are: Left Eye, Right Eye, Mouth, Nose and Face
- Flip - Option to flip the face inset texture horizontally or vertically
- Blend Mode - The blend mode of the inset. Commonly used blend modes are Multiply, Overlay and Soft Light
- Alpha - How transparent the face inset is
- Source Texture - Where the facial features are being pulled from. In most cases, this should be set to
Camera Output - Out. Border Rad - How large you'd like the copied region to be. A low number will be tight to the feature. A higher number will have more padding
- Inn. Border Rad. - How transparent the edges of the added region is
- Source Scale - The scale of the region texture
- UV Offset - The offset of the region texture from center
- Subdiv. Count - Determines how many vertices are drawn for the copied shape, thus controlling how smooth the shape of the copied region is