Remote Service Gateway
Overview
Spectacles offers a set of APIs that can be used alongside user-sensitive data — like the camera frame, location, and audio. By default, access to sensitive data is disabled when a Lens uses internet-connected components unless the user accepts the permission prompt or enables Extended Permissions for Experimental APIs.
Supported Services
OpenAI
Externally hosted by OpenAI
- Chat Completions - Generate conversational AI responses using GPT models (GPT-5, GPT-4o, GPT-4.1-nano, etc.)
- Image Generation - Create images from text descriptions using DALL-E
- Image Edit - Edit images by providing a prompt, base image, and mask
- Text-to-Speech - Convert text to natural-sounding speech audio with multiple voice options
- Realtime - Real-time conversational AI with low-latency voice capabilities (WebSocket)
Google Generative AI
Externally hosted by Google
Gemini
- Gemini Model - Access Google's Gemini large language models for multimodal AI (text, images, video)
- Gemini Live - Real-time conversational AI with voice and video capabilities (WebSocket)
Imagen
- Image Generation - Generate high-quality images from text prompts
Lyria
- Music Generation - Create original music compositions from text descriptions
Snap-Hosted APIs
Hosted directly by Snap
DeepSeek
- Chat Completions with DeepSeek-R1 Reasoning - Advanced AI chat with transparent step-by-step reasoning capabilities
Snap3D
- Text-to-3D - Generate 3D models (GLB) and assets from text descriptions and images, optimized for Spectacles. See the examples for details.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
Lens Studio v5.10.1 or later
Spectacles OS v5.062 or later
The APIs are only available on Spectacles.
Setup Instructions
API Token Configuration
The Remote Service Gateway requires API tokens to access different services. All tokens can be generated using the Remote Service Gateway Token Generator.
Generating Tokens
The Remote Service Gateway Token Generator plugin is available in the Asset Library under the Spectacles section. After installing the plugin, open the token generator from the Lens Studio Main Menu Windows -> Remote Service Gateway Token.
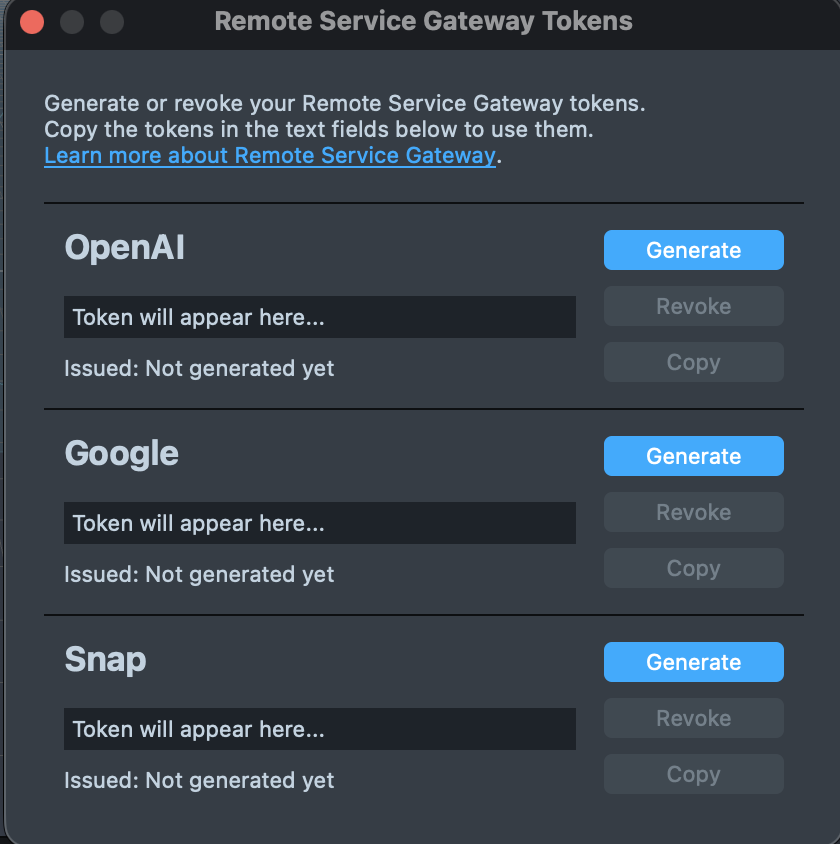
The token generator can create tokens for:
- Snap Token - Required for Snap-hosted APIs (DeepSeek and Snap3D)
- OpenAI Token - Required for OpenAI services (Chat Completions, Image Generation, Image Edit, Text-to-Speech, Realtime)
- Google Token - Required for Google GenAI services (Gemini, Imagen, and Lyria)
Use the Generate Token button to create tokens for the services you need. Each generated token can be copied to the clipboard using the copy button next to each token field. The generated tokens can be configured in RemoteServiceGatewayCredentials for use in your project.
Tokens have no expiration date, are tied to your Snapchat account, and can be used across multiple projects and computers. When generating a token on different computers, if a token already exists for your Snapchat account, the generator will display the existing token instead of creating a new one.
Tokens can be revoked through the Lens Studio Main Menu Windows -> Remote Service Gateway Token using the Revoke Token button if a new token needs to be generated.
Revoking tokens will invalidate Remote Service Gateway API usage for all existing Lenses that use those tokens. This action cannot be undone.
All API tokens are unique to your account and should be treated as confidential. Do not include tokens when sharing your project with others or committing code to version control systems.
Remote Service Gateway Package
The Asset Library under the Spectacles section contains the Remote Service Gateway package which includes RemoteServiceModule, helper scripts and examples for quick setup and use of the APIs. After generating your tokens using the Token Generator, you need to manually enter the appropriate API tokens (Snap, OpenAI, and/or Google) in the RemoteServiceGatewayCredentials component based on which services you plan to use.
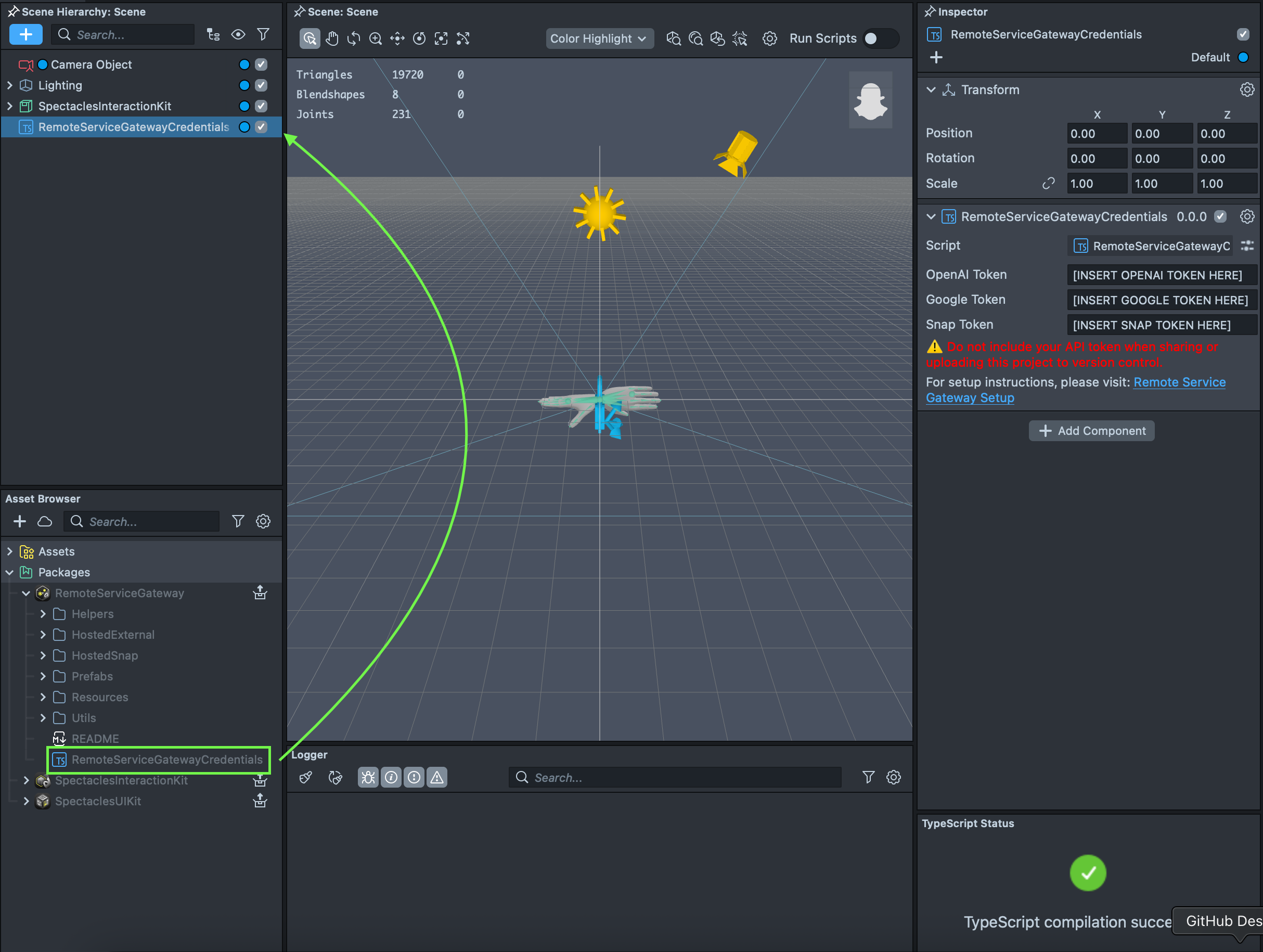
Examples
Assumes that you have already installed the Remote Service Gateway package from the Asset Library.
For more detailed examples, refer to the example prefab included in the Remote Service Gateway package available in the Asset Library or the AI Playground available in the Lens Studio Homepage Sample Project section.
OpenAI Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate OpenAI's chat completion API into Spectacles Lenses, allowing developers to send prompts with system instructions and user questions to GPT models.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { OpenAI } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/OpenAI';
@component
export class OpenAIExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.doChatCompletions();
});
}
doChatCompletions() {
OpenAI.chatCompletions({
model: 'gpt-4.1-nano',
messages: [
{
role: 'system',
content:
"You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
{
role: 'user',
content: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
],
temperature: 0.7,
})
.then((response) => {
print(response.choices[0].message.content);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
}
const OpenAI =
require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/OpenAI').OpenAI;
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
doChatCompletions();
});
function doChatCompletions() {
OpenAI.chatCompletions({
model: 'gpt-4.1-nano',
messages: [
{
role: 'system',
content:
"You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
{
role: 'user',
content: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
],
temperature: 0.7,
})
.then((response) => {
print(response.choices[0].message.content);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
Gemini Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate Gemini's Model API into Spectacles Lenses, allowing developers to send prompts with system instructions and user questions.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { Gemini } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Gemini';
import { GeminiTypes } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/GeminiTypes';
@component
export class GeminiExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.textToTextExample();
});
}
textToTextExample() {
let request: GeminiTypes.Models.GenerateContentRequest = {
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash-lite',
type: 'generateContent',
body: {
contents: [
{
parts: [
{
text: "You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
],
role: 'model',
},
{
parts: [
{
text: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
],
role: 'user',
},
],
},
};
Gemini.models(request)
.then((response) => {
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
}
const Gemini =
require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Gemini').Gemini;
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
textToTextExample();
});
function textToTextExample() {
let request = {
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash-lite',
type: 'generateContent',
body: {
contents: [
{
parts: [
{
text: "You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
],
role: 'model',
},
{
parts: [
{
text: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
],
role: 'user',
},
],
},
};
Gemini.models(request)
.then((response) => {
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
DeepSeek Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate DeepSeek's R1 Reasoning API into Spectacles Lenses, allowing developers to send prompts with system instructions and user questions.
Please be aware that DeepSeek's chat completions processing may require time to complete. Allow for extended response times when testing this functionality.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { DeepSeek } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/Deepseek';
import { DeepSeekTypes } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/DeepSeekTypes';
@component
export class DeepSeekExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.doChatCompletions();
});
}
doChatCompletions() {
let messageArray: Array<DeepSeekTypes.ChatCompletions.Message> = [
{
role: 'system',
content:
"You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
{
role: 'user',
content: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
];
const deepSeekRequest: DeepSeekTypes.ChatCompletions.Request = {
model: 'DeepSeek-R1',
messages: messageArray,
max_tokens: 2048,
temperature: 0.7,
};
DeepSeek.chatCompletions(deepSeekRequest)
.then((response) => {
let reasoningContent = response?.choices[0]?.message?.reasoning_content;
let messageContent = response?.choices[0]?.message?.content;
print('Reasoning: ' + reasoningContent);
print('Final answer: ' + messageContent);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
}
const DeepSeek =
require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/Deepseek').DeepSeek;
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
doChatCompletions();
});
function doChatCompletions() {
let messageArray = [
{
role: 'system',
content:
"You are an incredibly smart but witty AI assistant who likes to answers life's greatest mysteries in under two sentences",
},
{
role: 'user',
content: 'Is a hotdog a sandwich?',
},
];
const deepSeekRequest = {
model: 'DeepSeek-R1',
messages: messageArray,
max_tokens: 2048,
temperature: 0.7,
};
DeepSeek.chatCompletions(deepSeekRequest)
.then((response) => {
let reasoningContent = response.choices[0].message.reasoning_content;
let messageContent = response.choices[0].message.content;
print('Reasoning: ' + reasoningContent);
print('Final answer: ' + messageContent);
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
Imagen Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate Google's Imagen API into Spectacles Lenses, allowing developers to generate high-quality images from text prompts.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { Imagen } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Imagen';
import { GoogleGenAITypes } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/GoogleGenAITypes';
@component
export class ImagenExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
@input
imgObject: SceneObject;
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.generateImage();
});
}
generateImage() {
const request: GoogleGenAITypes.Imagen.ImagenRequest = {
model: 'imagen-3.0-generate-002',
body: {
parameters: {
sampleCount: 1,
addWatermark: false,
aspectRatio: '1:1',
enhancePrompt: true,
language: 'en',
seed: 0,
},
instances: [
{
prompt: 'A futuristic cityscape at sunset',
},
],
},
};
Imagen.generateImage(request)
.then((response) => {
print('Image generated successfully');
response.predictions.forEach((prediction) => {
let b64 = prediction.bytesBase64Encoded;
Base64.decodeTextureAsync(
b64,
(texture) => {
this.imgObject.getComponent('Image').mainPass.baseTex = texture;
},
() => {
print('Failed to decode texture from base64 data.');
}
);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Imagen generate error: ' + error);
});
}
}
const Imagen =
require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Imagen').Imagen;
//@input Asset.SceneObject imgObject
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
generateImage();
});
function generateImage() {
const request = {
model: 'imagen-3.0-generate-002',
body: {
parameters: {
sampleCount: 1,
addWatermark: false,
aspectRatio: '1:1',
enhancePrompt: true,
language: 'en',
seed: 0,
},
instances: [
{
prompt: 'A futuristic cityscape at sunset',
},
],
},
};
Imagen.generateImage(request)
.then((response) => {
print('Image generated successfully');
response.predictions.forEach((prediction) => {
let b64 = prediction.bytesBase64Encoded;
Base64.decodeTextureAsync(
b64,
(texture) => {
script.imgObject.getComponent('Image').mainPass.baseTex = texture;
},
() => {
print('Failed to decode texture from base64 data.');
}
);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Imagen generate error: ' + error);
});
}
Lyria Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate Google's Lyria API into Spectacles Lenses, allowing developers to generate original music from text descriptions.
Please be aware that Lyria's music generation may require significant time to complete. Allow for extended response times when testing this functionality.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { Lyria } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Lyria';
import { GoogleGenAITypes } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/GoogleGenAITypes';
import { DynamicAudioOutput } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/Helpers/DynamicAudioOutput';
@component
export class LyriaExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
@input
dynamicAudioOutput: DynamicAudioOutput;
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.generateMusic();
});
}
generateMusic() {
const musicRequest: GoogleGenAITypes.Lyria.LyriaRequest = {
model: 'lyria-002',
type: 'predict',
body: {
instances: [
{
prompt: 'An energetic electronic dance track with a fast tempo',
negative_prompt: 'vocals, slow tempo',
seed: 12345,
},
],
parameters: {
sample_count: 1,
},
},
};
this.dynamicAudioOutput.initialize(48000);
Lyria.performLyriaRequest(musicRequest)
.then((response) => {
print('Music generated successfully');
response.predictions.forEach((prediction) => {
let b64 = prediction.bytesBase64Encoded;
this.dynamicAudioOutput.addAudioFrame(Base64.decode(b64), 2);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Music generation failed: ' + error);
});
}
}
const Lyria = require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedExternal/Lyria').Lyria;
const DynamicAudioOutput =
require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/Helpers/DynamicAudioOutput').DynamicAudioOutput;
//@input ScriptComponent dynamicAudioOutput
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
generateMusic();
});
function generateMusic() {
const musicRequest = {
model: 'lyria-002',
type: 'predict',
body: {
instances: [
{
prompt: 'An energetic electronic dance track with a fast tempo',
negative_prompt: 'vocals, slow tempo',
seed: 12345,
},
],
parameters: {
sample_count: 1,
},
},
};
script.dynamicAudioOutput.initialize(48000);
Lyria.performLyriaRequest(musicRequest)
.then((response) => {
print('Music generated successfully');
response.predictions.forEach((prediction) => {
let b64 = prediction.bytesBase64Encoded;
script.dynamicAudioOutput.addAudioFrame(Base64.decode(b64), 2);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Music generation failed: ' + error);
});
}
Snap3D Example
This example demonstrates how to integrate Snap3D into Spectacles Lenses, allowing you to generate text to 2D to 3D assets.
Please be aware that Snap3D processing may require significant time to complete. Allow for extended response times when testing this functionality.
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
import { Snap3D } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/Snap3D';
import { Snap3DTypes } from 'RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/Snap3DTypes';
@component
export class Snap3DExample extends BaseScriptComponent {
onAwake() {
this.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
this.do3DGeneration();
});
}
do3DGeneration() {
Snap3D.submitAndGetStatus({
prompt: 'A cute cartoony hotdog character',
format: 'glb',
refine: true,
use_vertex_color: false,
})
.then((submitGetStatusResults) => {
submitGetStatusResults.event.add(([value, assetOrError]) => {
if (value === 'image') {
let imageAsset = assetOrError as Snap3DTypes.TextureAssetData;
//Apply imageAsset.texture;
} else if (value === 'base_mesh') {
let gltfAsset = assetOrError as Snap3DTypes.GltfAssetData;
//Apply gltfAsset.gltf;
} else if (value === 'refined_mesh') {
let gltfAsset = assetOrError as Snap3DTypes.GltfAssetData;
//Apply gltfAsset.gltf;
} else if (value === 'failed') {
let error = assetOrError as {
errorMsg: string;
errorCode: number;
};
print('Error: ' + error.errorMsg);
}
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
}
const Snap3D = require('RemoteServiceGateway.lspkg/HostedSnap/Snap3D').Snap3D;
script.createEvent('OnStartEvent').bind(() => {
do3DGeneration();
});
function do3DGeneration() {
Snap3D.submitAndGetStatus({
prompt: 'A cute cartoony hotdog character',
format: 'glb',
refine: true,
use_vertex_color: false,
})
.then((submitGetStatusResults) => {
submitGetStatusResults.event.add(([value, assetOrError]) => {
if (value === 'image') {
let imageAsset = assetOrError;
//Apply imageAsset.texture;
} else if (value === 'base_mesh') {
let gltfAsset = assetOrError;
//Apply gltfAsset.gltf;
} else if (value === 'refined_mesh') {
let gltfAsset = assetOrError;
//Apply gltfAsset.gltf;
} else if (value === 'failed') {
let error = assetOrError;
print('Error: ' + error.errorMsg);
}
});
})
.catch((error) => {
print('Error: ' + error);
});
}
Helper Utilities
The Remote Service Gateway package includes utility scripts to simplify media handling and AI integrations:
Media Processing Helpers
-
VideoController- Captures and encodes camera frames for visual AI processing. Provides formatted video data for APIs that support visual input (e.g., Gemini Live). -
MicrophoneRecorder- Manages microphone input and audio frame recording. Handles audio capture for real-time voice interactions. -
AudioProcessor- Buffers and formats audio data for external services. Processes audio streams into the appropriate format for AI APIs. -
DynamicAudioOutput- Handles playback of PCM16 audio from generative AI models. Enables real-time audio output from text-to-speech and voice generation APIs. Used in the Lyria example above for playing generated music.
Utility Classes
Event- Event system for managing callbacks and listenersPromisfy- Promise utilities for asynchronous operations
These helpers streamline integration with APIs requiring audio/visual input or supporting audio output. See the example prefab included in the Remote Service Gateway package for usage demonstrations.
Known Limitations
- The OpenAI chat_completions endpoint does not support streaming.
- For the Gemini LiveAPI, only
models/gemini-2.0-flash-live-preview-04-09is supported. - Imagen image editing and upscaling features are not currently supported.